Impulsive Transformator
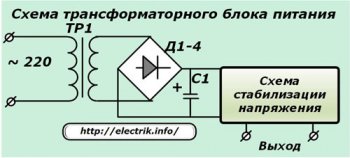 By altering the position of the sub-constructors, the stabilization scheme manages the output voltage.
By altering the position of the sub-constructors, the stabilization scheme manages the output voltage.
Impulse Nutrition Units (PSI)
Such constructive developments have been widespread several decades ago and have become increasingly popular in electrical appliances by:
- Access to a common element base;
- reliability in performance;
- possibilities to increase the working range of output voltages.
Virtually all impulse power sources are slightly different in design and one typical for other devices.
Modern feeding units of different types with appropriate parameters and characteristics can be obtained by using an online service to search for ChipHunt--
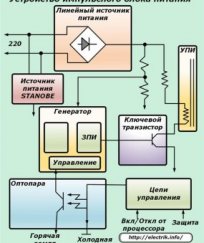
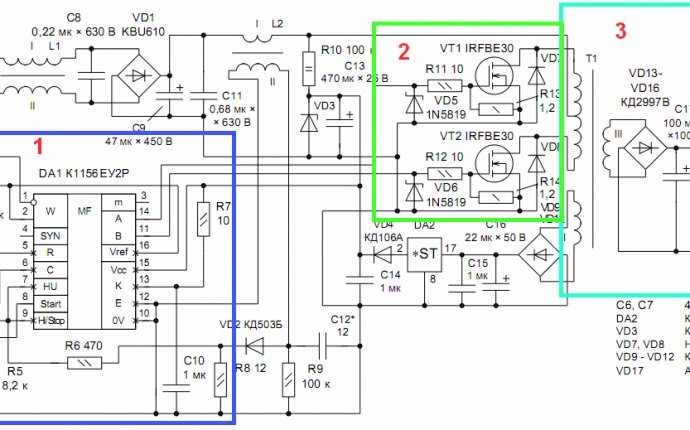
The main components of the power sources are:
- An online straightening device assembled from: input throes, an electromechanical filter that cuts the interference and connects the static to condensers, a network protector and a diode bridge;
- Filter storage capacity;
- Key force tranche;
- Rearing generator;
- Transistor feedback scheme;
- Optopara;
- An impulse power source with a secondary refrigerated voltage to transform into a power chain;
- Straight diodes of the exit scheme;
- output voltage chain management, e.g. 12 volts with a substrate manufactured on optore and transistors;
- Filter capacitors;
- Power throttles which act as voltage correction and diagnostics on the network;
- We're going to have a weekend.
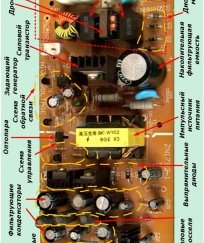
An example of an electronic fee for such an impulse power unit, with a brief symbol of the elementary base, is shown in the picture.
How the impulse power unit works.
The impulse power unit provides a stabilized power supply through the use of the principles of interaction between the components of the superstructure.
The network voltage is 220 volts from the wires connected to the stitch. Its amplitude is slacked by a chassis filter by using capacitors that contain a beer of about 300 volts and is removed by a interference filter.